READING OF FINANCIAL STATEMENT
AUTHOR :Muhammed Mustafa C T
https://taxgtower.blog/brqblog/my_post_view/READING-OF-FINANCIAL-STATEMENT-1-286-423PURPOSE OF FINANCIAL STATEMENT
Structured representation of the financial position & Financial performance of an entity.
IT PROVIDES INFORMATION ABOUT THE ENTITY'S:
(a) Assets: resource owned or controlled by an entity CURRENT & CAPITAL
(b) Liabilities; legal obligations or Debt owed to another person or company
(c) Equity: the value attributable to the owners of a business (Asset- Liability)
(d) Income and expenses, including gains and losses
(e) Contributions by and distributions to owners in their capacity as owners
(f) Cash flows: shows how much cash is generated and used during a given time period.
This information, along with other information in the notes, assists users of financial statements in predicting the entity's future cash flows and, in particular, their timing and certainty.
- ASSETS: resource owned or controlled by an entity CURRENT & CAPITAL
- Liabilities ; Liabilities are legal obligations or debt owed to another person or company
- Equity: equity is the value attributable to the owners of a business ( Asset-Liability)
- Cash flows ; shows how much cash is generated and used during a given time period.
PARTS OF FINANCIAL STATEMENT
A complete set of financial statements comprises:
- A balance sheet as at the end of the period ;
- A statement of profit and loss for the period;
- Statement of changes in equity for the period;
- A statement of cash flows for the period;
- Notes, comprising significant accounting policies and other explanatory information;
- comparative information in respect of the preceding period as specified
- Investments, Profits, Good Corporate Governance
- Significant bearing on investment decision of a
- stakeholder Also decides quantum of his investment
- Ensures financial transparency to the stakeholders
- Observance of universally accepted reporting norms
AUDITOR'S REPORT
- Audit is mandatory for all companies incorporated under the Companies Act, 2013, i.e. all Private Limited or Public Limited Companies.
- Only a Chartered Accountant is authorized to carry out audit. In fact, the report of statutory auditor is addressed to the shareholders of the company.
- Every Audit begins with the report which is given by the auditor after thorough examination of the books of accounts and all related records and documents. Once this report is given, the accounts of the company are finalized and thereafter no change can be made in the accounts of a company.
- Based on the study of the records of a company, a statutory auditor is required to give his opinion on the following important aspects:
- Whether the Balance Sheet and Profit & Loss Account have been prepared as per the provisions of the Companies Act and as per normally accepted accounting principles.
- Whether the Balance Sheet gives a true and fair view of the profit or loss of the company
THINGS TO BE LOOOKED AT IN AUDITOR'S REPORT
- Stock of Raw Material & Finished Goods: The statutory auditor is required to comment upon the following aspects of physical verification of finished goods, raw material, stores & spares.
- Whether physical verification was conducted.
- Whether periodicity is reasonable.
- Whether procedure is reasonable and adequate
- Whether any material discrepancies were noticed.
- How the discrepancies were dealt with in accounts
- Whether valuation is fair
- Whether physical verification was conducted.
THINGS TO BE LOOOKED AT IN AUDITOR'S REPORT
Generally, the auditors confirm to the various points raised in above paras. The tax investigator should, therefore, call for physical verification statements and see the discrepancies and their treatment in accounts. In case of perpetual inventory system, the variation is adjusted in consumption on regular basis; therefore, year-end stock verification report may not be very relevant. In that case monthly adjustment journal voucher should be verified. In case of qualified opinion on these matters, the tax investigator should be very careful and need to go further in greater detail
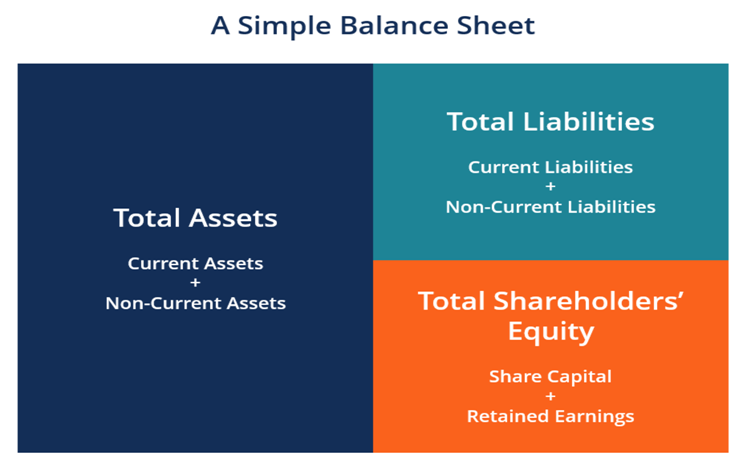
BALANCE SHEET
- The Balance Sheet is a statement showing the financial position of the business on a particular date. The financial position is exhibited by a statement of assets and liabilities. Analysis of Balance Sheet can reflect the Liquidity / Profitability / Turn Over / Debt Finance / Valuation Position of a concern.
- The Balance Sheet is drawn up from the balances of those ledger accounts which remain after the accounts relating to revenue and charges have been closed by transfer to Manufacturing, Trading and Profit & Loss Accounts. Such balances are assets or liabilities, or are regarded temporarily as such for Balance Sheet purposes.
- It Is Prepared On The Basis Of Schedule 3 Of Companies Act
- Capital Goods - If any capital asset is used for effecting taxable and non-taxable supply ITC as per Rule 43.
- Blocked Credit - Section 17(5) : If expenditure relating to any goods or services is in connection with a building or civil structure and is capitalized : No ITC is available.
- Investments - in Financial Assets : Transactions in securities is exempt supply - ITC to be reversed as per provisions of Section 17(3)
- Common use - if Inputs are used for Taxable and Non Taxable purpose ITC to be availed as per Rule 42
RULE 42 FOR REVERSAL OF CREDIT
- Rule 42 :- Manner of determination of input tax credit in respect of inputs or input services and reversal thereof
- EXCLUSIVE USE FOR EXEMPT ACTIVITY ITC NOT ALLOWED
- EXCLUSIVE USE FOR TAXABLE ACTIVITY ITC ALLOWED FULLY
- ONLY COMMON CREDIT TO BE APPORTIONED IN THE FOLLOWING RATIO FOR DISALLOWANCE
- EXEMPT TURNOVER / TOTAL TURONVER (T.O. to exclude taxes)
- ADD for DISALLOWANCE 5% of ITC where BUSINESS USE and NONBUSINESS USE BOTH EXIST FOR SOME INWARD SUPPLIES
- FOR DETAILS REFER RULE 42
KEY POINT TO BE LOOKED INTO BALANCE SHEET
- Inventories
- (a) ITC in respect of Inventories (Inputs) is available to the registered person - Inputs must be used for business purpose.
- (b) No claim of ITC in respect of Goods in Transit - ITC is available only when the goods are received
- (a) ITC in respect of Inventories (Inputs) is available to the registered person - Inputs must be used for business purpose.
- Loans Rule 42 / 43 - For a Banking Company or an NBFC - ITC - as per Rule 42/Rule 43 or 50% of the eligible ITC on inputs, capital goods and input services on monthly basis.
- Trade Receivables :- See Debtor's ledgers for identifying this issue; IGST Act - Service supply to be treated as Zero rated supply i.e. EXPORT - But payment must be received in convertible foreign currency. Otherwise, taxes to be paid on such services.
- Other current / Non-Current Assets
- ITC Balance: Input Tax Credit as appearing in the financial statements must tally with ITC appearing in Electronic Credit Ledger. Reconciliation essential If short in Account Debit from ECL.
- Advances given to suppliers:- For services RCM liability to be examined advances given for supply of services. Not applicable for Goods though (Noti No. 66/2017 15.11.2017).
- Deposits If adjustable against some supply, to be treated as consideration received in advance. Tax liability accrues on the date when such advance is received or at the time of adjustment, as applicable.
- Trade Payable:-
- Check if liability is outstanding for more than 180 days - ITC to be got reversed in such cases
- Section 16 ITC Can be reclaimed after making payment
- Advance received from customers :-
- Goods:- GST not to be discharged Notification No. 66 / 2017 Central Tax dated 15th November 2017.
- Services:- GST to be paid on such receipt of advance.
- Contingent Liability:-
- Guarantees given to related parties
- Schedule I of the CGST Act-GST to be discharged in cases where supply is provided to the related person -even without consideration.
- Schedule I of the CGST Act-GST to be discharged in cases where supply is provided to the related person -even without consideration.
- Other current Liabilities:-
- Examine Output Tax liability Reconcile this amount with the one in Electronic Liability Register
- Disclosure
- GST is levied at the point of supply i.e. at the time of sales
- GST not to be included in Revenue.
- Revenue may not be indicated as including GST.
- For 17-18 it will be combination of both.
- Beware when you compare different years one of which is before GST or partially non GST.
- Disclosure
- GST is levied at the point of supply i.e. at the time of sales
- GST not to be included in Revenue.
- Revenue may not be indicated as including GST.
- For 17-18 it will be combination of both.
- Beware when you compare different years one of which is before GST or partially non GST.
- Inventory valuation
- Thus inventory value includes GST to the extent no ITC availment or no refund claim is proposed to be preferred. In other cases no GST element will be part of inventory value.
- Common inputs and input services for business and non-business activities.
- To be Careful in certain situations:-
- Depreciation claimed on tax portion/element;
- Tax paid under section 10 (inward supplies from composition registrations;
- Input / input services / capital goods are used for personal purposes;
- Input/input services/ capital goods used for exempted supply);
- Restricted credits u/s 17(5) of the CGST Act
- Depreciation claimed on tax portion/element;
PROFIT AND LOSS ACCOUNT
The following are some of the important points, which should be kept in mind while studying a Profit & Loss Account:
- There are different Schedules for most of the headings, therefore Profit & Loss Account needs to be studied by referring to these Schedules.
- Details of Profit & Loss Account should be studied along with notes to the accounts forming part of the final accounts.
- A comparative study of figures with previous year should be made to find out unusual variation
- Value of clearances as per GSTR-1 return filed with the GST department should be compared with sales value shown in the Profit & Loss Account.
- It should be noted that sales as per the Profit & Loss Account may include GST or any other amount like packing & forwarding charges collected separately in the invoice.
- Statement on accounting policies enclosed with the Balance Sheet and Profit & Loss Account may show the method of accounting sales, i.e., whether it includes GST or any other element.
- Similarly, if sales are made through depots or C & F Agents, the sales value as per GSTR-1 returns and as per Profit & Loss Account may not tally. A reconciliation statement should be sought from the Company to compare the two figures.
Scrutiny of Other Incomes
This is one of the most important area which a tax investigator is required to analyze very carefully. It may include income under the following heads:
- Sale of Scrap;
- Insurance Claim;
- Profit on sale of Fixed Assets;
- Interest / Dividend received;
- Commission received;
- Royalty received;
- Technical knowhow or Technical consultancy charges;
- Erection and Commissioning Charges;
- Training Income;
- Miscellaneous Income;
- Freight / Insurance Recovered;
Sale of Scrap
- A tax investigator should ascertain the series of sales invoice used for sale of scrap. Other documents like Debit Notes or journal vouchers may also be used for recording the sale of scrap.
- This fact can be found out from the study of the ledger account.
- A tax investigator should examine these documents to confirm payment of GST.
- Insurance claim may be lodged for damage or destruction of raw material, work in progress, finished goods or capital goods. A tax investigator should examine the exact details of such claims.
- The following types of insurance claim cases should be examined in detail:
- damage of raw material before receipt in the factory.
- damage of raw material in the factory.
- damage of Work-in-Progress or finished goods in the factory.
- damage of capital goods in the factory
- damage of raw material before receipt in the factory.
TO BE CHECKED :-
- cases where the insurance claims have been received.
- cases where claims have been lodged even though the claims have not been finally sanctioned by the insurance company.
- claim applications should be studied to find out details of quantity claimed to have been damaged, value & excise duty/ GST claimed in the insurance claim.
- where GST has also been claimed in the insurance claim in case of loss of finished goods lying in the factory, reversal of ITC should be made.
INCOME :-
- Reconciliations Aggregate all incomes Include after examination credits in Debit accounts (expenditure/Purchase) Tag them with ITC Reversal Required Output GST Liability
- Exclude those constitute to Zero rated supplies without payment of GST
- Check which of them are excluded from purview of application of proportionate reversal of ITC
- Rest all are required to be considered for Total Turnover and apportionment of ITC based on such turnovers
- Compare Taxable Turnover with Value of supplies on payment of GST as declared in the periodical returns
- Compare value of Zero rated supplies with such Zero rated Value of supplies as declared in the periodical returns
- Any difference in above comparisons is to be highlighted
- Ind AS 16- Fixed Assets.
- Section 18(3) Claim of depreciation under Income-tax Act, 1961, on that part of value which represents the tax component of the value/cost of Assets (capital goods and plant and machinery), Tax Credit of the said tax component shall not be allowed.
- Section 18(3) Claim of depreciation under Income-tax Act, 1961, on that part of value which represents the tax component of the value/cost of Assets (capital goods and plant and machinery), Tax Credit of the said tax component shall not be allowed.
- IND AS 20-Accounting for Government Grants
- Section 15(2)(e) of CGST Act => the value of supply shall include subsidies directly linked to the price excluding subsidies provided by the Central Government and State Governments.
- Inferred that Government Grants would not be treated as part of value of supply for the purpose of GST.
REVENUE
- A Reconciliation of Revenue
- Appearing in the Financial Statements with the GSTR
- Returns of the Registered Person.
- Appearing in the Financial Statements with the GSTR
- Classification under GST of each Goods or Services to be checked along with the applicable GST Rate at the time of supply of particular goods or services.
- Revenue includes unbilled revenue in statement of Profit and Loss. No GST to be discharged on such revenue reported in the financial statement.
- Cases where adjustments in the value of revenue on case of companies preparing financial statements as per IND AS.
- The amount of Revenue as per Financial statements and the GST Returns may deviate in such cases like schemes provided to customers to be deducted from Revenue in the Statement of Profit and Loss.
- The amount of Revenue as per Financial statements and the GST Returns may deviate in such cases like schemes provided to customers to be deducted from Revenue in the Statement of Profit and Loss.
- Nature of Revenue to be identified, i.e. the supply is Taxable or Exempt or Non-GST Supply.
- In case of Exports, whether the same is under LUT or made with payment of IGST to be checked.
Other Income
- Supply test as per the provisions of Section 7 to be considered to check whether any Income is taxable as per the GST or not.
- Income in nature of sale of Investments It refers to the situation where the transactions in securities (Investments) has been made by the registered person, ITC to be reversed in such cases as per the provisions of section 17(3) since the same is exempt supply under GST.
EXPENSES
- Input Tax Credit availed by the registered person need to be evaluated from the fact that the same is used in course or furtherance of business. If any expenses on which GST is charged by supplier or RCM is discharged, the same should be related to the business of the registered person.
- Section 17(5) of the CGST Act has specifically mention certain cases where a registered person is not eligible to take credit even the same is used in course or furtherance of business such as:
- motor vehicles (seating less than 13 persons), vessels, aircraft with some exceptions including cost of maintenance and security of such conveyances;
- food and beverages, outdoor catering, beauty treatment, health services, cosmetic and plastic surgery, rent/ lease of above conveyances and life/health insurance
- membership of a club, health and fitness center
- travel benefits extended to employees on vacation such as leave or home travel concession;
- WCT services when supplied for construction of an immovable property.
- goods or services or both received by a taxable person for construction of an immovable property (other than plant or machinery)
- goods or services or both on which tax has been paid under section 10
- goods or services or both received by a non-resident taxable person except on goods imported by him
- goods or services or both used for personal consumption
- goods lost, stolen, destroyed, written off or disposed of by way of gift or free samples.
- motor vehicles (seating less than 13 persons), vessels, aircraft with some exceptions including cost of maintenance and security of such conveyances;
- Generally, the expenses are debited to the statement of profit and loss statement, however there may be cases where a particular expense ledger is credited like :-
- Recovery of expenses incurred where some may show it as separately under Other Income head and others may credited the same to the corresponding expense head. These type of credit entries in the profit and loss to be checked.
- Prior Period items
- Prior period expenses debited to P & L - Remember time limit to claim ITC(Return for September after the end of the related financial year or filing Annual return or One Year from the date of document, whichever is earlier).
- Such Taxable Income credited to the P & L - Interest Liability - If taxes are also not paid on due dates.
- Prior period expenses debited to P & L - Remember time limit to claim ITC(Return for September after the end of the related financial year or filing Annual return or One Year from the date of document, whichever is earlier).
- There is a disclosure requirement in the financial statement relating to expenditure in foreign currency. The same disclosure would help in identifying the cases of import of services, if any,
NOTES TO ACCOUNT
- BY WAY OF A NOTE the following information shall also be disclosed.
- Value of imports calculated on C.I.F basis by the company during the financial year in respect of
- Raw materials;
- Components and spare parts;
- Capital goods;
- Raw materials;
- Expenditure in foreign currency during the financial year on account of royalty, know-how, professional and consultation fees, interest, and other matters;
- Value of imports calculated on C.I.F basis by the company during the financial year in respect of
- Total value of all imported raw materials, spare parts and components consumed during the financial year and the total value of all indigenous raw materials, spare parts and components similarly consumed and the percentage of each to the total consumption;
- The amount remitted during the year in foreign currencies on account of dividends, with a specific mention of the total number of non-resident shareholders, the total number of shares held by them on which the dividends were due and the year to which the dividends related;
- Earnings in foreign exchange classified under the following heads, namely:-
- Export of goods calculated on F.O.B. basis;
- Royalty, know-how, professional and consultation fees;
- Interest and dividend;
- Other income, indicating the nature thereof
- Export of goods calculated on F.O.B. basis;
- The entity is also expected to report in notes to accounts, any event happening after the ending date of the period for which report is prepared but which has taken place before the date on which report is presented and which is likely to have significant effect on the business being conducted by the entity.
- Incident of Fire / Incident of Theft / Incident of Flood
- Whether ITC stands reversed?
- Whether capital goods have been damaged? Whether cleared as scrap?
- Whether the insurance claim includes element of taxes of which ITC stands claimed?
- Material Account
- Write off of inventory due to obsolescence or for any other reason?
- Stock Verification irregularities noticed ?
- Use for non-business activities ?
- Whether ITC stands reversed?
LEDGERS AND ACCOUNTS
Any Rules for Selection of Accounts for Scrutiny ?
- No fixed rules - Companies manufacture different products Follow different accounting policies - Different marketing policies Use different types of accounting software packages.
- The selection of accounts also depends upon the audit plan.
- Following aspect be kept in mind while selecting the accounts for scrutiny:
- Credit entries in raw material or other input purchase account
- Credit entries in expense account
- Income accounts
- Unusual accounts
- Important Debtors and Creditors
- Debtors
- Any debits by vouchers other than invoice ? Examine GST impact.
- Creditors
- Any debits by vouchers other than payments ? Examine GST impact
Any Rules for Selection of Accounts for Scrutiny ?
- Gross Trial Balance - Study description of income accounts
- Accounts like interest on investment, or dividend may not be of much relevance from the GST point of view. The scrutiny of these accounts should be done from the following two angles:
- Nature of income - GST is liable to be paid or added to the assessable value of supply of goods or services. If yes, whether all such supplies have suffered payment of GST ?
- Whether income is of a type which has effect on ITC availment ?
(Sec-44AB of IT ACT)
- Every person carrying on business or profession get his accounts of such previous year audited by an accountant before the specified date and furnish by that date the report of such audit in the prescribed form duly signed and verified by such accountant and setting forth such particulars as may be prescribed, :-
- For carrying on business, if his total sales, turnover or gross receipts, as the case may be, in business exceed or exceeds one crore rupees in any previous year; or
- carrying on profession shall, if his gross receipts in profession exceed fifty lakh rupees in any previous year; or
- carrying on the business shall, if the profits and gains from the business are deemed to be the profits and gains of such person under section 44AE or section 44BB or section 44BBB, as the case may be, and he has claimed his income to be lower than the profits or gains so deemed to be the profits and gains of his business, as the case may be, in any previous year; or
- carrying on the profession shall, if the profits and gains from the profession are deemed to be the profits and gains of such person under section 44ADA and he has claimed such income to be lower than the profits and gains so deemed to be the profits and gains of his profession and his income exceeds the maximum amount which is not chargeable to income-tax in any previous year; or
- (e) carrying on the business shall, if the provisions of sub-section (4) of section 44AD are applicable in his case and his income exceeds the maximum amount which is not chargeable to income-tax in any previous year,
- For carrying on business, if his total sales, turnover or gross receipts, as the case may be, in business exceed or exceeds one crore rupees in any previous year; or
Disclaimer:
(Note: Information compiled above is based on my understanding and review. Any suggestions to improve above information are welcome with folded hands, with appreciation in advance. All readers are requested to form their considered views based on their own study before deciding conclusively in the matter. Team BRQ ASSOCIATES & Author disclaim all liability in respect to actions taken or not taken based on any or all the contents of this article to the fullest extent permitted by law. Do not act or refrain from acting upon this information without seeking professional legal counsel.)
In case if you have any querys or require more information please feel free to revert us anytime. Feedbacks are invited at brqgst@gmail.com or contact are 9633181898. or via WhatsApp at 9633181898.
